China’s State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) announced on November 28, 2025, that it had ordered BYD (HKG:1211) to recall 88,981 Qin PLUS DM-i vehicles produced between 2021 and 2023 due to battery pack consistency defects. The issue involves variation in the behavior of individual cells within the battery pack, which can result in reduced pure-electric driving range and potential power interruption during operation.
The Qin PLUS DM-i has been a top-selling A-segment plug-in hybrid model in China and BYD’s best selling car model. As of October 2025 year-to date, BYD delivered 305,110 Qin PLUS.
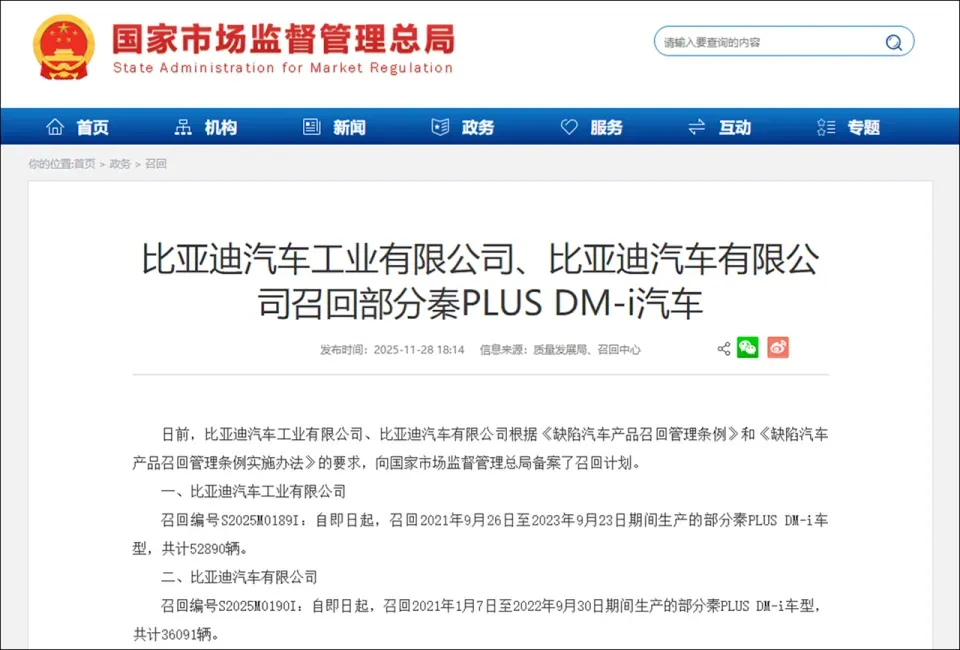
Source: SAMR
SAMR initiated an investigation after receiving user complaints regarding premature range loss, eventually identifying non-uniform charging and discharging behavior among battery cells. The regulator noted that this defect could cause certain cells to reach depletion earlier than expected, leading to a sudden loss of electric-mode power while the vehicle is in motion.
One owner who purchased a 2023 Qin PLUS DM-i reported that the vehicle, rated for 55 km (34 miles) of pure-electric range, could only travel slightly above 20 km (12 miles) before the battery was depleted. Initial responses from retail service outlets attributed this to normal degradation, but the recall confirms underlying cell-level inconsistencies affecting a wider batch of vehicles.
Advertisement – Continue scrolling for more
BYD stated it will conduct remote software diagnostics on affected vehicles and replace battery packs when necessary. The company indicated that replacement scheduling may require more than two weeks due to parts availability and service capacity. The recall follows a series of battery-related actions in 2025 across China’s new-energy vehicle segment. Complaints regarding battery degradation and stability have climbed, and the Qin PLUS DM-i ranked among the ten most-complained models for battery issues this year.
Industry data cited in 2025 show that leading Chinese automakers record an average battery-consistency deviation of around 5%, compared with approximately 2% at leading international benchmarks. Variance in battery-cell capacity can increase over time; a Qin PLUS DM-i with an estimated 3% deviation at delivery may see this gap expand to approximately 15% after three years of use. Such divergence leads to faster-than-expected range loss and power instability, and has contributed to falling used-NEV valuations across the market.
Advertisement – Continue scrolling for more
The high production pace of 2021–2023, when the Qin PLUS DM-i experienced rapid sales growth, may have contributed to pressure on production screening and quality control cycles. Raw-material prices were elevated during that period, and manufacturers across the industry were cutting costs through reduced testing and calibration steps in battery-production workflows. These measures have now prompted broader scrutiny from regulators.
Battery-safety concerns have not been limited to BYD. In October 2025, a fire involving a Li Auto MEGA in Shanghai circulated widely on social media platforms. Li Auto later filed a recall plan affecting 11,411 units of the 2024 model year after identifying insufficient corrosion resistance in coolant that may cause leakage. Although no direct link to the fire was confirmed, the company committed to replacing coolant, battery packs, and front electrical-control systems in affected vehicles.
Advertisement – Continue scrolling for more
China has intensified regulatory requirements for EV battery safety. Since October 2025, automakers must report battery-related fire incidents within 24 hours, and all software or battery-parameter adjustments must be traceable. A new national standard for EV battery safety, GB 38031-2025, will take effect in July 2026. The standard requires that battery packs must not ignite or explode, introduces bottom-impact testing, and mandates short-circuit testing after 300 fast-charge cycles. Vehicles failing these requirements cannot be sold.
Advertisement – Continue scrolling for more
